Translating Literature with LLMs: Maintaining Consistency on Named Entities And Integrating External Knowledge
Dec 207, 20200· ·
0 min read
·
0 min read
Jiarui Liu
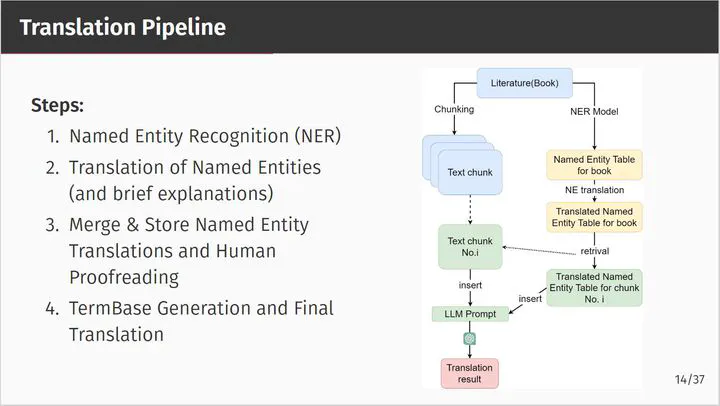 Termbase insert translation pipeline
Termbase insert translation pipelineAbstract
In literary translation, the accurate and consistent translation of named entities, such as character names and significant proper nouns, is essential. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in translation tasks; however, they often struggle to maintain consistency over long texts due to limitations in context windows and computational budgets. This study introduces an efficient approach that combines the advanced capabilities of LLMs with human translation practices using In-Context Learning (ICL) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). We integrating Termbase, pre-editing methods, and external knowledge sources such as Wikipedia into LLMs and our findings demonstrate that this hybrid method significantly improves both the consistency of named entities and the overall quality of translation, offering a practical solution for literature machine translation.
Type